Time and Motion
Did you know that the time we keep here on Earth is related to motion within the Solar System??!
What is a DAY?
A day is the length of time it takes a planet to complete one rotation on its axis. However, this rotation can be measured with respect to the location of the Sun (from noon to noon is a solar day), or the stars (a sidereal day).
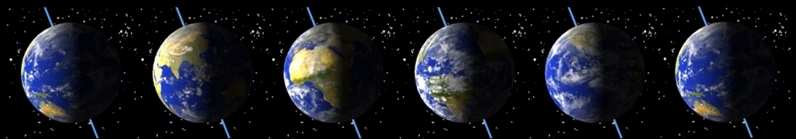
Sequence showing the daily rotation of the Earth. The rotation axis is the pale blue line through the north and south poles.
An average solar day is 24 hours, which is the time from noon to noon. (The exact legnth of a solar dat changes slightly because of the oval-shaped orbit of the Earth around the Sun.) A sidereal day is about 4 minutes shorter and lasts for 23 hours 56 minutes 4.091 seconds.
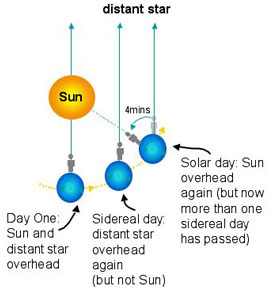
A sidereal day is one Earth rotation as seen by the distance stars, and is about 4 minutes shorter that a solar day, which is the time from noon to noon.
See day, solar day, sidereal day.
What is a MONTH?
A calendar month (like January, February, March...) is not really related to astronomy. But a lunar month is. This is the time it takes the Moon to orit the Earth. But this too can be measured with respect to the location of the Sun or the distance stars. It takes the Moon 29.5 days to go through a lunar cycles, from full moon to full moon. This is called a synodic period.

A lunar month is the time from full moon to full moon, which is 29.5 days or one synodic period.
A sidereal period is the time it takes the Moon to orbit the Earth as seen by the distance stars, and is 27.3 days.

A sidereal period is one lunar month as seen by the distance stars, and is shorter than a synodic period - the time from full moon to full moon.
lunar phases.
What is a YEAR?
A year is the amount of time it takes for the Earth to orbit the Sun. Our calendar year is usually 365 days, and 366 days every four yeras (which we call a leap year). The real orbital period of the Earth around the Sun is called a tropical year and it takes 365.2419 days.
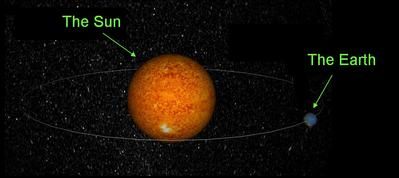
It takes one year, or about 365 days, for the Earth to orbit the Sun.
Because one tropical year (365.24219 days) is not exactly a calendar year (365 days), every four years we need to add one day (a leap year), so that the average year is 365.25 days. The leap year was introduced in 46 BC by the Romanaemporer Julius Caesar (following the advice of his astronomers) to try to better match the calendar with the annual observations of the stars in the sky.
See year, leap year
Last updated: Thursday, 03-May-2012 23:00:34 AEST
Back to Sarah's SiS page




