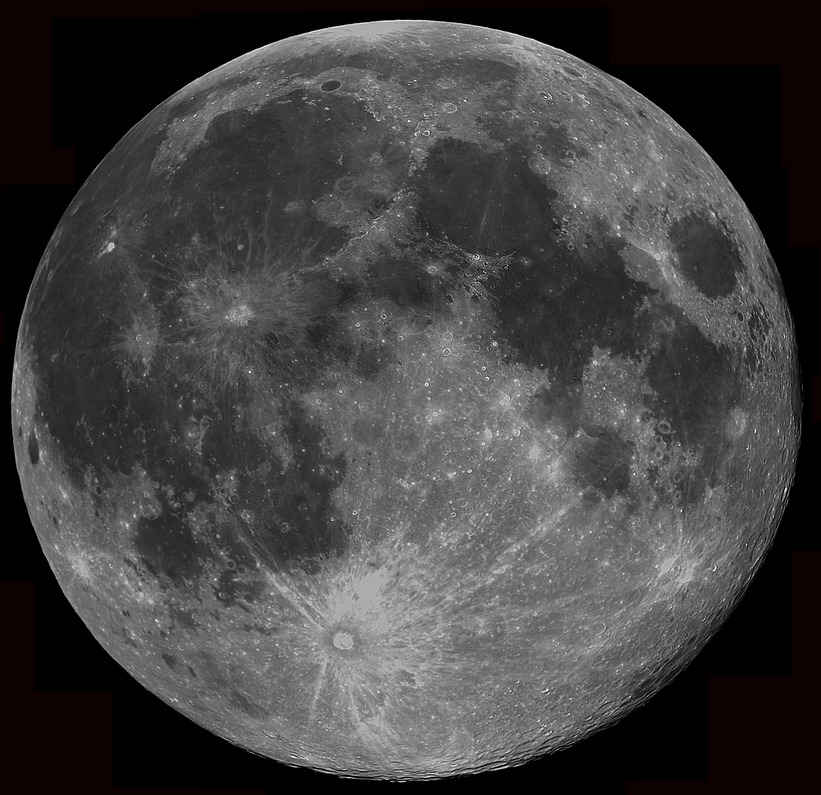
 | The largest craters on the Moon, like Mare Imbrium which is over 1100 km in diameter, have been flooded by lava and we can only see parts of their circular outline. Because these dark "mare" (which means 'sea') have few craters on them, they must be younger that the surrounding areas. |  |
 | Simple craters like Moltke (which is 6.5 km in diameter and 1.3 km deep), have a smooth bowl-like shape with smooth walls. Most small craters less than about 15 km in diameter are simple craters. |  |
 | Complex craters like Tycho (which is 85 km in diameter and 4.5 km deep), have well defined crater rims and a central peak. Most craters between 20 and 175 km in diameter and complex craters. |  |
 | Larger impact basins, like the 310 km diameter Schrödinger crater and 330 km diameter Mare Orientale, generally have ring-shaped uplifted regions in the centre of the crater. Impact basins are usually at least 300 km in diameter. |  |



