anthropic cosmological principle: Only a restricted range of possible universes is favourable for the evolution and existence of life (and thus us, the observers).
baryon: A massive elementary particle made up of three quarks. Neutrons and protons are baryons.
baryonic matter: Ordinary matter as we know it consists largely of baryons, as opposed to hypothetical matter that might theoretically exist. Both kinds have mass, and either kind can be dark matter.
Big Bang: A model of the Universe beginning at very high density and temperature, which expands and cools to become the Universe we observe now.
blackbody: An object with a constant temperature that absorbs all radiation that hits it.
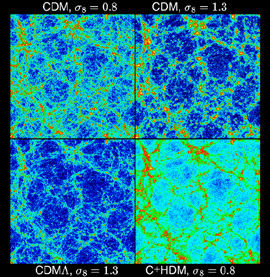
cold dark matter (CDM): A type of dark matter that was moving at much less than the speed of light 10,000 years after the Big Bang. CDM would exist as exotic particles that only weakly interact with radiation and baryons. CDM would make matter clump into small-scale units with galaxies forming first. Clusters and superclusters would form later.
closed universe: A cosmological model in which the Universe is finite, and will eventually recollapse. The density of this Universe is more than the critical density.
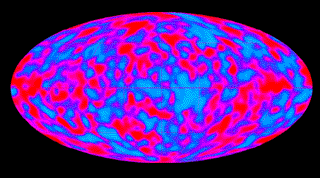
CMB: Cosmic Microwave Background radiation, also CMBR, CBR and the "3 K blackbody radiation". Radiation left over from the Big Bang which has cooled by expansion to a temperature slightly less than 3 degrees above absolute zero.
cosmic strings: Tubelike configurations of energy that might arise in the early universe (and remain in our present Universe). They may exist as line-like defects in space-time.
cosmological constant: A term in Einstein's general relativity equations that works in the opposite sense of gravity. Einstein used it to force the existence of a static Universe. Usually denoted by the capital Greek letter Lambda when expressed with units of inverse length squared, or by the lower-case Greek lambda when normalized to the critical density (like Omega).
cosmology: The study of the contents, structure, and evolution of the universe from the beginning of time to the infinite future.
critical density: The density of the Universe necessary so the expansion rate of the Universe is just barely sufficient to prevent a recollapse. Omega is the mass density of the Universe normalised to units of the critical density.
dark matter: A form of matter that does not emit light, absorb light, or scatter light. Its only interactions are gravitational. So far, it has not been detected. This "extra-mass" is strongly inferred to exist due to the fast motions of galaxies in clusters, and of stars in galaxies.
density: The amount of matter in a volume divided by the volume, so the units are grams per cubic centimeter. Water has a density of 1 gram per cubic centimeter.
Doppler: 19th century physicist who discovered the variation in the wavelength of waves caused by motion of the source.
electromagnetic force: One of the four forces of nature. Electromagnetic interactions hold electrons in atoms, hold atoms in molecules, and are used in all electronic devices.
electroweak force: A unified force that combines the electromagnetic and weak nuclear interactions. Predicted by Weinberg and Salam, experimentally verified by Rubbia and van der Meer.
escape velocity: The minimum velocity that will allow an object to escape from a gravitational field.
general relativity: Einstein's laws of physics in which gravity is described by a curvature of space-time.
Gyr: Gigayear, or one billion years.
grand unified theory (GUT): A model for unifying the strong nuclear force, the weak nuclear force, and the electromagnetic force at very high energies. Ultimately, it is hoped to extend GUT to incorporate gravity (possibly by superstrings) to create a theory of everything (TOE). Several such GUTs have been proposed, but not yet experimentally verified.
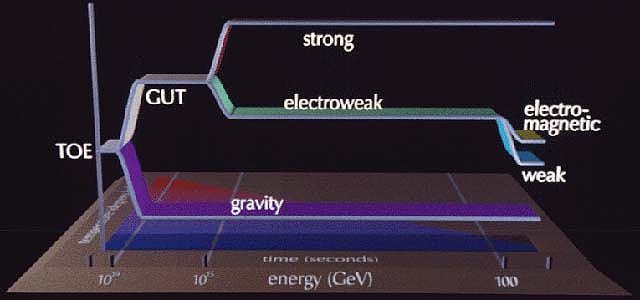
gravity: One of the four forces of nature. The force depends on the masses of particles and their separations. Gravity has allowed galaxies, stars and planets to form.
gravitational potential: The gravitational energy per unit mass of a particle, equivalent to the acceleration of gravity times the height in ordinary circumstances on the surface of the Earth.
homogeneous: The same at all locations.
horizon: The edge of the visible Universe, but not the edge of the Universe since the Universe has no edge.
hot dark matter (HDM): A type of dark matter that was moving at close to the speed of light 10,000 years after the Big Bang. An example of a hot dark matter candidate is the massive neutrino. HDM would produce large-scale structures first (supercluster, clusters) which would then fragment into individual galaxies.
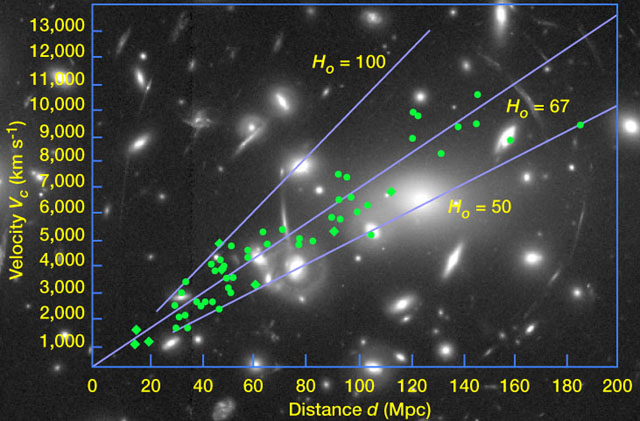
Hubble constant: Or H0, the ratio of velocity (v) to distance (D) in the expansion of the Universe, so v = H0D. The "0" [pronounced "naught"] on H0 means the current value, since the Hubble "constant" changes with time (but it is the same everywhere in the Universe at a given time).
inflationary scenario: A modification of the Big Bang model in which a large cosmological constant exists temporarily early in the history of the Big Bang (around t=10-35 secs), leading to a rapid accelerating expansion of the Universe, which is then followed by the normal Big Bang model with a decelerating expansion.
isotropic: The same in all directions. Anisotropic - not isotropic. Anisotropy - difference between different directions. In the standard color scheme for CMB anisotropy maps measured by the COBE DMR, red shows areas of the sky that are warmer, while blue shows the cooler regions.
Local Group: The system of galaxies to which our Milky Way galaxy belongs. It is a group of over 30 galaxies, dominated by two large spirals (our Galaxy and Messier 31, the Andromeda galaxy).

non-baryonic: Not made up of neutrons, protons (ie. atoms) and thus not like any of the known chemical elements.
Nucleon: A neutron or a proton - one of the particles inside an atomic nucleus.
nucleosynthesis: Formation of atomic nuclei by nuclear reactions either in the Big Bang or in stellar interiors. Hydrogen, Deuterium, Helium and Lithium are made early on in the Big Bang. Heavier elements (eg. Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen) are produced in stellar interiors.
Omega: The ratio of the density of the Universe to the critical density (needed for eventual collapse).
open universe: A cosmological model in which the Universe is infinite and will expand forever.
parsec: A unit of distance used by astronomers, corresponding to a parallax of one arc-second. Equal to 3.085678 x 1013 kilometers, or 3.26 light-years. kpc: 1000 parsecs; Mpc: 1 million parsecs.
photon: A quantum of light, having wave and particle-like properties.
Planck time/length: t=10-43 secs. It is the shortest time interval that can exist; if two events are separated by less than this, we cannot say which comes before and which after. Prior to t=10-43 secs after the Big Bang, Einstein's General Relativity theory of gravity breaks down and a quantized theory is needed. Similarly, the related Planck length of 10-33 cm is the length scale below which space as we know it ceases to exist and becomes quantum foam.
QSO: quasi-stellar object. The first discovered QSO's were radio sources, leading to the name quasi-stellar radio sources, or QSRS, or quasars. These objects look like stars on an image of the sky, but their spectra show strong emission lines at high redshift. The redshift means that quasars are very far away, and are thus the most luminous objects in the Universe.
quantum fluctuations: The uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics leads to all allowed interactions occuring with some probability.
quantum foam: A foamlike structure of space that probably makes up the cores of singularities, and that probably occurs in ordinary space on scales less than the Planck length.
radiation era: The era up to 300,000 years after the Big Bang when radiation was the dominant constituent of the Universe.
redshift: The Doppler shift for objects receding from the Earth causes the wavelengths of light to get longer, and hence shift into the red part of the spectrum.
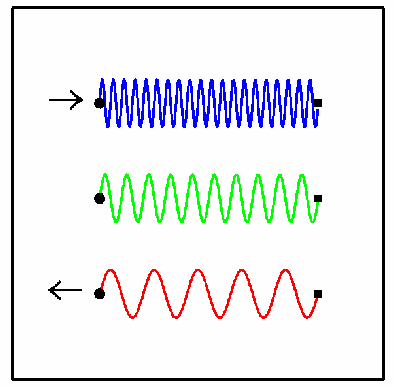
redshift (gravitational): Light is emitted at a longer (redder) wavelength in a gravitational field than in the absence of a gravitational field. Earth's gravity induces a gravitational redshift of 1 part in 109; a white dwarf star, about 1 part in 104.
singularity: A infinitely dense region of space-time where the known laws of physics break down, and the curvature of space becomes infinite.
space-time: The four-dimensional "fabric" that results when space and time are unified.
spectrum: Result of spreading out light by wavelengths. A rainbow is a natural spectrum. The eye is sensitive to waves from violet at 380 nm (nm: nanometre or 1x10-9 metre) wavelength to red at 700 nm wavelength, but astronomers now study electromagnetic radiation from gamma rays through X-rays, ultraviolet, violet, blue, green, yellow, orange, red, infrared and radio waves.
Steady State (Theory): An elegant model of the expanding Universe with constant density and physical properties. Matter must be continually created to maintain the constant density. Numerous observations have discredited the theory.
strong nuclear force: One of the four forces of nature. The strong nuclear force holds the particles in the nucleus of atoms together.
string (theory): An attempt to construct a model of elementary particles from one-dimensional "strings" rather than the standard zero-dimensional "points" of conventional particle physics.
superstring (theory): A 26-dimensional (or 10-dimensional) string that has a line-like topology in which all fundamental forces are unified. It is possible that our 3-dimensional Universe collapsed out of such a string. Strings have not yet been observed.
vacuum energy density: Quantum theory requires empty space to be filled with particles and anti-particles being continually created and annihilated. This could lead to a net density of the vacuum, which if present, would behave like a cosmological constant.
weak nuclear force: One of the four forces of nature. The weak nuclear force is responsible for radioactive decay as well as the fusion reactions in the Sun that provide heat and light for the Earth.
WIMP: Acronym for a Weakly Interacting Massive Particle, a possible form for cold dark matter.
zero point energy: The uncertainty principle does not allow a quantum mechanical system to have a definite position and definite velocity at the same time. Thus a harmonic oscillator like a pendulum or a mass on a spring has a minimum energy that is larger than zero, since zero energy would require a definite position to zero the potential energy and a definite (zero) velocity to zero the kinetic energy. This minimum energy is 0.5*h*f, where h is Planck's constant and f is the frequency of the oscillator.